Courtesy of Kansas State University Anthropology professor Michael Wesch, in a talk that is beautiful, moving, and deeply insightful.
Tag: Learning
My Three Priorities for 2022
OK. It’s a New Year. Now what?
This feels like an especially relevant question when the problems we face – in 2022 and beyond – seem so overwhelming.
Here in America, we’ve entered fascism’s legal phase. Around the world, the climate emergency advances, unabated. And for the third year in a row, the COVID pandemic rages on.
Against such odds, what are we to do?
In my mind, there’s only one way to avoid the WALL-E-y soporific stupor that awaits us:
We must make 2022 the Year of the Network.
In fact, this shift has been remaking the scientific community for years; scholars in fields ranging from biology to ecology have revised the metaphors they use to describe their work, and begun to affirm, as physicist Fritjof Capra says, “that partnership – the tendency to associate, establish links, and maintain symbiotic relationships – is one of the hallmarks of life.”
Medical scholars like Dan Siegel agree. “Relationships are the crucible in which our lives unfold as they shape our life story,” he explains, “molding our identity and giving birth to the experience of who we are, and liberating — or constraining — who we can become.”
That’s not just flowery prose; it’s how living systems operate in the natural world — by existing and creatively organizing within and between a boundary of self. Although this boundary is semipermeable and ensures the system is open to the continuous flow of matter and energy from the environment, the boundary itself is structurally closed.
A cell wall is a good example. It’s the boundary that establishes its system’s identity, distinguishes it from and connects it to its environment, and determines what enters and leaves. But because this meaning of “boundary” is as much about what it lets in as what it keeps out, the end result of this arrangement, according to the German biologist Andreas Weber, is a notion of self in which “every subject is not sovereign but rather an intersubject — a self-creating pattern in an unfathomable meshwork of longings, repulsions, and dependencies.”
In the daily whir of our personal and professional lives, that means we need one another more than ever – and not just the people who make up our proximite physical pods, but those of us who, thanks to these dialectical technologies, can now foster meaningful connections (and expand our respective self-creating patterns) across miles and time zones and traditions.
“When you form groups,” writes Iain Couzin, who leads the Centre for the Advanced Study of Collective Behavior, “you suddenly have a network system where social interactions exist. We have traditionally assumed that intelligence resides in our brains, in the individual animal. But we have found the first evidence that intelligence can also be encoded in the hidden network of communication between us.”
This is the profound lesson we need to learn from nature — a lesson that is equally true at the smallest scale.
“In the quantum world,” explains Margaret Wheatley, “relationship is the key determiner of everything. Nothing exists on its own or has a final, fixed identity. We are all bundles of potential. Relationships evoke these potentials. We change as we meet different people or are in different circumstances.”
To that end, then, let’s make 2022 the year when we provide one another with three things in abundance:
- New Rituals
One of the most important features of rituals, psychologist Rebecca Lester explains, is that they not only mark time; they create time. “By defining beginnings and ends to developmental or social phases, rituals structure our social worlds and how we understand time, relationships, and change.”
This is why we created the Seed + Spark Network – as a space for new rituals in this highly liminal period of our lives. For all of us, life as “normal” is distinctly over. Yet we’ve yet to discover whatever our new normal will be. “So we wait,” Lester writes, “in this in-between state, betwixt and between, neither here nor there, suspended.”
We are not built to live this way – in endless liminality, with life and time unmarked.
So we need new rituals, and although each of us will have our own, I hope you’ll join us each Wednesday night throughout this new year -– when we can mark the time, make new connections, and evoke our own bundles of potential. See you there?
- New Ideas
We won’t get out of the mess we’re in by applying the same logic that got us here in the first place.
We need a new path, and a new story.
Whereas for centuries we’ve all lived under the same systemic trappings of modern life (from capitalism to communism), today we require a new kind of order, and a new source of strength. “Anything not built for a network age — our politics, our economics, our national security, our education — is going to crack apart under its pressures,” journalist Joshua Cooper Ramo suggests. “Our era is one of connected crises. Relationships now matter as much as any single object. And puzzles such as the future of United States-China relations or income inequality or artificial intelligence or terrorism are all network problems, unsolvable with traditional thinking.”
In response, we’ve designed a deck of cards for humanity that will, we hope, help you fall (back) in love with the natural world, become more knowledgeable about living systems, and apply those insights creatively to address the myriad problems that require our sustained, urgent attention.

Here they are, in digital form. Try them out, see what they spark, and share what you learn with the rest of us.
- New Relationships
Most importantly, we need one another – both those who are already a part of our circle, and those we have yet to meet.
In a living system, everything is connected. There are no parts to be exchanged or fixed. Critical connections, not critical mass, are what matters most.
How, then, can we deepen both the quantity and the quality of the connections in our lives?
“Exalted we are,” wrote the recently-departed American biologist E.O. Wilson, “risen to be the mind of the biosphere without a doubt, our spirits uniquely capable of awe and ever more breathtaking leaps of imagination. But we are still part of Earth’s fauna and flora, bound to it by emotion, physiology, and, not least, deep history.”
So let’s be more intentional in this New Year in the ways we weave ourselves together.
Let’s face the problems of the world with our collective strength and wisdom. And let’s make this a year of new rituals, new ideas, and new relationships that can help light the path to building a better world, by design.
“Behind the cotton wool is hidden a pattern,” Virginia Woolf said. “The whole world is a work of art . . . Hamlet or a Beethoven quartet is the truth about this vast mass that we call the world. But there is no Shakespeare, there is no Beethoven; certainly and emphatically there is no God.
“We are the words; we are the music; we are the thing itself.”
Why do we have 180 days of school?
School’s out for summer again.
Why is that, exactly?
The answer is in our newest #AskWhy video — and it might surprise you.
WHY DO WE STILL TREAT EDUCATION LIKE IT’S 1906?
Why do we still use a 19th-century invention— The Carnegie Unit—to determine if our kids are ready to graduate in 2019?
Also, what the heck is a Carnegie Unit?
Watch the latest video in our #AskWhy series — a series that has now been viewed by more than ten million of you — to find out.
The same way may not be the best way.
Diverse by Design: Episode 3 (Never Teach Alone)
Powerful learning is a relational act; it never occurs alone.
Why, then, do we expect our teacher to hone their craft in isolation?
In episode 3 of the four-part series, Diverse by Design, we meet two of Crosstown High’s inaugural class of teachers, and learn why they believe that co-teaching is the only way to go. So be prepared: their perspective may change the way you think about the future of learning — and what it will require.
Diverse by Design: Episode 2 (Project Based Learning)
How active should learning be? How relevant? And what is required of adults if they are serious about expecting that kids will have a different experience — and a different feeling — in that thing we call ‘school’?
In a new four-part series from 180 Studio, we witness one community’s efforts to answer those questions.
In the city of Memphis, in a formerly abandoned Sears warehouse, a new school, Crosstown High, is aspiring to model something that hasn’t been seen before — a version of school that looks nothing like the schools most of us attended or experienced, and an explicit commitment to weave together a community of young people who embody the full range of Memphis’s social, economic, and ethnic diversity.
This is Diverse by Design.
Diverse by Design: Episode 1 (The First Day of School)
How do you reimagine something that has looked the same for generations? And what does a diverse society require — and need — in order to support a shared commitment to the common good?
In a new four-part series from 180 Studio, we witness one community’s efforts to answer both questions.
In the city of Memphis, in a formerly abandoned Sears warehouse, a new school, Crosstown High, is aspiring to model something that hasn’t been seen before — a version of school that looks nothing like the schools most of us attended or experienced, and an explicit commitment to weave together a community of young people who embody the full range of Memphis’s social, economic, and ethnic diversity.
This is Diverse by Design. I hope you’ll watch, share, & comment . . .
The Science of the Human Brain
It is the most complex living system in the known universe, built of hundreds of billions of cells, each as complicated as a city.
It is the primary author of the deeply personal story we tell ourselves about who we are and why we are here.
And it never, ever, shows us the world as it truly is — only as we need it to be.
This is the conundrum of the human brain, which is why understanding its peculiar science is a prerequisite towards our ability to imagine, and then build, a better world.
Consider this: Human beings — or, for that matter, any other life form on earth — see only what has helped them survive in the past. The way we make sense of the present is still being shaped by the innovations, fears and assumptions our ancestors made hundreds, thousands, even millions of years ago. And yet our success as a species has occurred not in spite of our inability to see reality, but because of it.
As neuroscientist Beau Lotto puts it, human beings didn’t evolve to see the world objectively; they evolved to “not die.” And all living things have managed to “not die” thus far by developing different perceptual overlays on the same planetary backdrop.
Bats developed echolocation.
Cephalopods learned to change colors.
Birds got GPS.
And we developed a wet computer with a parallel processor — otherwise known as a bi-hemispheric brain.
Why did our brains evolve that way, with a singular blueprint stamped out twice? No one knows for sure, although psychiatrist Iain McGlichrist believes it happened to help us “attend to the world in two completely different ways, and in so doing to bring two different worlds into being,” and two different ways of surviving life’s slings and arrows.
“In the one,” he explains, “we experience — the live, complex, embodied, world of individual, always unique beings, forever in flux, a net of interdependencies, forming and reforming wholes, a world in which we are deeply connected. In the other we ‘experience’ our experience in a special way: a ‘re-presented’ version of it, containing now static, separable, bounded, but essentially fragmented entities, grouped into classes, on which predictions can be based.
“These are not different ways of thinking about the world,” McGilchrist claims. “They are different ways of being in the world. If the left hemisphere is the hemisphere of ‘what’, the right hemisphere, with its preoccupation with context, the relational aspects of experience, emotion and the nuances of expression, could be said to be the hemisphere of ‘how.’”
Who we perceive ourselves to be is a mashup of these different perceptual overlays — ostensibly equal parts logic and emotion. And yet the reality of the modern world, says McGilchrist, is that our way of seeing has gotten out of balance.
For a number of reasons, we have become left-hemisphere heavy.
“My thesis is that for us as human beings there are two fundamentally opposed realities, two different modes of existence; that each is of ultimate importance in bringing about the recognizably human world; and that their difference is rooted in the bihemispheric structure of the brain. It follows,” he asserts, “that the hemispheres need to cooperate, but I believe they are in fact involved in a sort of power struggle, and that this explains many aspects of contemporary Western culture.”
Is it possible to bring ourselves back in balance? Harvard neuroscientist Jill Bolte Taylor would say yes — and she would know. In 1996, a blood vessel burst in the left half of her brain. “In the course of four hours,” she explains, “I watched my brain completely deteriorate in its ability to process all information.”
Because Taylor had spent her adult life studying the brain’s intricate architecture, she was uniquely suited to observe how the stroke was affecting her. What she discovered has huge implications for how all of us think about who (& why) we are in the world.
But first, a refresher course:
On one side of our brain, there is the right hemisphere, which is designed to help us remember things as they relate to one another. “To the right mind,” Taylor says, “no time exists other than the present moment, and each moment is vibrant with sensation. By design, our right mind is spontaneous, carefree, and imaginative. It allows our artistic juices to flow free without inhibition or judgment.” And it gives us the sense that we are indistinguishable, infinite, and interconnected.
By contrast, our left hemisphere organizes the world for us in a linear and methodical way. “Here,” says Taylor, “the concept of time is understood as either past, present or future, and our left brain thrives on details. Here, we use words to describe, categorize, define, and communicate about everything we see.” And here, we find the part of ourselves that feels most distinct — the part that proclaims, ‘I am,’ apart from the world.
Because Taylor’s stroke occurred in the left side of her brain, her right hemisphere was left unchecked by its usual counterbalance. As a result, she experienced a drastically different way of seeing the world (and her role in it). “I no longer perceived myself as a single, a solid, an entity with boundaries that separated me from the entities around me. Everything around us, about us, among us, within us, and between us is made up of atoms and molecules vibrating in space. Although the ego center of our language center prefers defining our self as individual and solid, most of us are aware that we are made up of trillions of cells, gallons of water, and ultimately everything about us exists in a constant and dynamic state of activity.
“My left hemisphere had been trained to perceive myself as a solid,” she explained, “separate from others. Now, released from that restrictive circuitry, my right hemisphere relished in its attachment to the eternal flow. I was no longer isolated and alone. My soul was as big as the universe and frolicked with glee in a boundless sea.”
For Taylor, the lesson is not that one hemisphere is better than the other; indeed, there is a reason our brain evolved this way — which is, simply, to integrate two contradictory yet complementary ways of seeing the world: one holistic and boundless, the other segmented and bound.
Rather, the lesson comes when we accept, as Beau Lotto puts it, that “the world out there is really just our three-dimensional screen. Our receptors take the meaningless information they receive; then our brain, through interacting with the world, encodes the historical meaning of that information, and projects our subjective versions of color, shape and distance onto things.
“Meaning is a plastic entity,” he reminds us, “much like the physical nature of the brain, which we shape and reshape through perceptual experiences. It is critical to understand that the meaning of the thing is not the same as the thing itself.”
Believing is seeing, more than seeing is believing. And so we will never change the story of how we learn and live unless we become aware of the way our brains are always trying to ensure that we “not die” — by providing us with a coherent story about our lives, a story that our brain works around the clock to create.
A story that is never, ever, accurate.
To see differently, we must learn to see seeing differently. “The more aware I remain about what my brain is saying and how those thoughts feel inside my body,” Taylor tells us, “the more I own my power in choosing what I want to spend my time thinking about and how I want to feel. If I want to retain my inner peace, I must be willing to consistently and persistently tend the garden of my mind moment by moment, and be willing to make the decision a thousand times a day.”
The clearer we are about the science of the human brain, in other words, the greater the chance we can appreciate the art of individual identity.
It is the most wondrous thing we have discovered in the universe, and it is us.
2019: The Year of Living Emergently?
We’re doing it again.
2019 is barely a week old, yet everyone seems to be searching for the singular person, policy or program that can restore order and usher in the better world we seek. From the excitement over the looming presidential race (and the promise of a return to normalcy) to the anticipation of the pending Mueller report (and the vision of a president in handcuffs), we are hardwired to hope for the sweeping solution, the quick fix, the reset button.
In reality, life works differently. What if we started to work in closer accordance with life?
What if we made 2019 the year of living “emergently?”
Emergence is not a word we hear or use often, yet it is the dynamic origin of development, learning and evolution, and we see evidence of its existence in everything from our cells to our cities. Indeed, the conditions for emergence flow from the reciprocal relationship that exists between any living form and its environment. A single ant, following the chemical trail of its neighbors to carve out a vital, completely decentralized role in a teeming colony. An adaptive software system, seeking patterns in individual behavior that shape which banner ad you see. A human stem cell, self-organizing into increasingly more complicated structures based on the behavior of its neighbors. Or even a solitary Tunisian fruit vendor, whose decision to set himself ablaze eventually sets the entire Arab world on fire.
As Steven Johnson writes in his book on the subject, the capacity for emergent systems to learn and grow “derives from their adherence to low-level rules. . . Emergent behaviors are all about living within the boundaries defined by rules, but also using that space to create something greater than the sum of its parts.”
In that sense, the central features of emergent systems outline a set of rules from the natural world that are both timeless and timely:
Give and receive feedback.
Pay attention to your closest neighbors.
Seek order, not control.
Start anywhere, and follow it everywhere.
It’s the songline of life itself — the deeply resonant story that flows through all living systems, including our own. And in a world that is becoming increasingly interwoven, and at a moment in history when the promise and peril of artificial intelligence are becoming more than just a sci-fi script, our ability to shift to a more emergent way of thinking may just be the difference between survival and extinction. As Johnson puts it, “our ability to capture the power of emergence will be closer to the revolution unleashed when we figured out how to distribute electricity a century ago. Almost every region of our cultural life was transformed by the power grid; the power of self-organization — coupled with the connective technology of the Internet — will usher in a revolution every bit as significant.”
Like the natural systems that surround us, the human systems we inhabit — from our schools to our cities to our political parties — are in a state of continuous dynamic balance. These systems are not done to us — we are the ones who create and perpetuate them, despite our protestations of innocence. (As the theoretical physicist David Bohm once put it, “Thinking makes the world and then says, ‘I didn’t do it.’”)
And so we cannot underestimate our individual and collective power to consciously create the conditions that make our system’s transformation in the direction we desire more likely.
It is literally that simple — and that complicated.
What, then, would it mean to make 2019 the year of living emergently?
For starters, it would mean resisting the urge to pin all of our hopes on any “singular solution.” Stop pretending that removing Donald Trump from office will restore a set of moral principles to American culture. Stop viewing ourselves as blameless pawns in someone else’s end game. Stop waiting for someone else’s policies to empower us to do our best work. And start working where you can, how you can, and with whom you can.
Although a better world depends on all of us, the work towards its creation begins with each of us. Transformation is first and foremost an inside job. And how we are at the small scale is how we are at the large scale.
We see evidence of these principles in practice throughout the natural world — although perhaps in no more stirring form than a murmuration of starlings. What words can do justice to the magic of as many as a million birds, flying and weaving as one?
Improvisatory choreography? Elegant chaos? Symphonic cacophony?
There is no familiar way to make sense of this natural phenomenon — both what they do and how it makes us feel when we see one. Yet this flocking behavior of the birds the ancient Romans believed foretold the will of the Gods — indeed, the word auspicious comes from the Latin auspicium, or “divination by observing the flight of birds” — is a natural manifestation of a set of principles for organizing complex behavior, and an observable phenomenon that runs counter to the way we human beings have made sense of the world for as long as anyone can remember. And thanks to the work of researchers, we now know that individual starlings all obey the same few flight rules:
Watch your seven nearest neighbors.
Fly toward each other, but don’t crowd.
And if your neighbor turns, turn with them.

Why do they do this? According to one of the studies, “when uncertainty in sensing is present, interacting with six or seven neighbors optimizes the balance between group cohesiveness and individual effort.” By following this rule of seven, the birds become part of a dynamic system in which each individual part combines to make a whole with emergent properties. This collective behavior allows the birds to gather information on their surroundings and self-organize toward an ideal density, one in which optimal patterns of light and dark are produced that can deliver information to the entire flock (and protect them from predators). The closer each bird pays attention, the safer — and more cohesive — the entire flock becomes.
Of course, this sort of swarming behavior is not unique to starlings. Many different animals, from birds and insects to fish and mammals, have been observed in their own form of a swarm. So what can this behavior teach us about ourselves, our organizations, and our ability to change the story of the way we work and learn?
According to Andreas Weber, author of The Biology of Wonder, “the spirit of poetic ecology is the spirit of swarms. To understand the individual, we need to understand its environment, and each through the other. We have to think of beings always as interbeings.
“We are a swarm ourselves,” Weber writes, “and we form swarms. A swarm does not have intelligence; it is intelligence. In this respect, a swarm (or a murmuration) is an intensified counterpart of ourselves. It is what we are and what we try to imagine with our conscious thinking. Swarms are solidified feeling. The swarm is — and in its being living dynamics and their expression are welded together in one single gesture.”
A murmuration, then, is more than just a metaphor for thinking differently about organizational behavior; it’s a reminder, in physical form, that our own bodies, cultures and classrooms are governed by the same rules.
As Weber puts it, “we see gestalts of the living that behave according to simple organic laws mirroring the great constellation that every living being has to cope with: to persist, to be close to the other, but not so close as to collide with him. These are the principles of poetic forms that are so thorough we can even teach them to a computer. They are the primary shapes of a poetics of living things.”
So let’s stop waiting for Godot. Let’s make 2019 the year in which we plant a thousand Trojan horses — future seeds of creative destruction that can, when the time is right, assume a different form, attack our most intractable rituals and assumptions about the systems we inhabit, and usher in a different way of being that is more in line with both the modern world and the modern brain.
Applying these principles to the way we organize ourselves will change the way we feel and act. It may even change the way we dream. “My dream is a movement with such deep trust that we move as a murmuration,” says author and activist Adrienne Maree Brown. “The way groups of starlings billow, dive, spin, and dance collectively through the air. Each creature tuned in to its neighbors. There is a right relationship, a right distance between them — too close and they crash, too far away and they can’t feel the micro-adaptations of the other bodies. Each creature is shifting direction, speed and proximity based on the information of the other creatures’ bodies. Imagine our movements cultivating this type of trust and depth with each other, having strategic flocking in our playbooks.”
We can imagine. And we can flock more strategically — but only when we recognize that the work begins with each of us, at the scale of the individual, now.
The Most Famous Nursery Schools in the World — And What They Can Teach Us
Reggio Emilia, a mid-sized city that sits roughly halfway between Milan and Bologna, is not your grandmother’s Italy.
For starters, it’s more hardscrabble than picturesque — heavily graffitied, with streets and buildings that feel weathered and worn from everyday use. And although you’ll still find the charming clock tower, the cobblestone streets and the Renaissance-era churches in the city center, you’ll also find a city in which one out of five residents is not from Italy itself, but places as far-flung as Ghana and Nigeria, Morocco and Albania, Yemen and Syria.
It is, in short, a microcosm of the changing face of Italy, and of the wider world: nascent, uprooted, and precariously perched between worlds and worldviews.
Why, then, is it also the home to the finest nursery schools in the world?


Recently, I traveled there to find out — along with more than 300 other educators from around the world. We were part of an international study group, scores of which regularly visit Reggio’s integrated public system of more than eighty infant/toddler and early childhood centers to bear witness to what has been created here — and wonder how it can be replicated elsewher
Because Reggio schools don’t exist anywhere else in the world — the closest you’ll find are schools that say they’re “Reggio-inspired” — they’re not well known outside of progressive education circles. But for those that do know, a visit to Reggio is akin to a pilgrimage to Mecca. And after spending five days there, walking the city’s streets, listening to lectures, and visiting several of its schools, I can see why.
Reggio Emilia is a city of altars — to childhood, to imagination, and to the spirit of shared governance and democratic participation. It is magical, but not in a precious way; it is revolutionary, but only because it has had the time and space to evolve; and it is illustrative, but not because it is prescriptive or straight-forward. In Reggio, the whole is always more that the sum of its parts. There are no shortcuts. And yet the path is as clear as can be.
To understand why, you must first travel back to 1945, when, after four years of worldwide war and two decades of domestic terrorism, a group of local residents made an unexpected (and unintended) discovery: one tank, six horses, and three trucks that were left behind by fleeing Nazi troops.
After some discussion, it became clear that by selling what they had found, the townspeople could underwrite an initial investment in their post-war future, and begin to write a new history in the wake of all that had been lost.
The men wanted to build a cinema. The women, a school.
Fortunately, the women won, and within weeks, the construction was underway. A young man named Loris Malaguzzi heard what was happening, and hopped on his bicycle to see for himself. “There were piles of sand and bricks,” he recalled, “a wheelbarrow full of hammers, shovels and hoes. Behind a curtain made of rugs to shield them from the sun, two women were hammering the old mortar off the bricks.
“We’re not crazy!” they exclaimed, unprompted. “If you really want to see, come on Saturday or Sunday, when we’re all here. We’re really going to make this school!”
For Malaguzzi, an elementary school teacher in a nearby town who would in time become the ceremonial leader of the the Reggio network, it was a life-changing moment. “It forced everything back to the beginning. It opened up completely new horizons of thought. I sensed that it was a formidable lesson of humanity and culture, which would generate other extraordinary events. All we needed to do was to follow the same path.”
The bedrock of that path was illuminated by a disturbing wartime lesson about humanity. “Mussolini and the fascists made us understand that obedient human beings are dangerous human beings,” he explained. “When we decided to build a new society after the war we understood that we needed to have schools in which children dared to think for themselves, and where children got the conditions for becoming active and critical citizens.”
Consequently, after seven decades of tinkering and revision, what a visitor will see in Reggio’s schools today are a series of design choices and principles that run counter to the way most of the world does ‘school.’
The goal is not knowledge; it’s communication
In Reggio schools, all adults believe that all children have at their disposal a hundred different languages — and that typically, “the school steals ninety-nine.” By languages, these adults do not mean merely the use of words, but also clay, paper, color, joy, imagination — anything that can help a child communicate his or her inner thoughts with the people around them. “We have not correctly legitimized a culture of childhood,” says Lella Gandini, a longtime Reggio teacher, “and the consequences are seen in all our social, economic, and political choices and investments.”
To counter this, Reggio’s schools are relentlessly child-centered — not to achieve notable results in literacy and numeracy, but to achieve notable qualities of identity formation and to ensure that all children know how to belong to a community. “Our approach offers children the opportunity to realize their ideas are different and that they hold a unique point of view,” said Gandini. “At the same time, children realize that the world is multiple and that other children can be discovered through a negotiation of ideas. Instead of interacting only through feelings and a sense of friendship, they discover how satisfying it is to exchange ideas and thereby transform their environment.”
I know, I know. It sounds amazing, but how do you actually teach that? What’s the curriculum in a Reggio school?
The curriculum is not fixed; it’s emergent
By design, Reggio schools were created to protect children from what Malaguzzi called the ‘prophetic pedagogy,’ or an education built on predetermined knowledge that got delivered bit by bit — a format Malaguzzi felt was humiliating for both teachers and children because of the ways it denied their ingenuity and emergent potential.
Consequently, Reggio teachers have no predetermined curricula (as the behaviorists would like), but neither do they work as constant improvisers. Instead, every year each school delineates a series of related projects, some short-range and some long. These themes serve as the main structural supports, but then, as Malaguzzi says, “it is up to the children, the course of events, and the teachers to determine whether the building turns out to be a hut on stilts or an apartment house or whatever. The teachers follow the children, not plans.”
To see this in action is part of what makes Reggio so magical, and the central feature it requires is a very different notion on the part of adults as to what their central role is, and is not. In this sense, teachers (and there are two in every classroom) are not there to deliver content, but to activate the meaning-making competencies of all children. As Malaguzzi put it, “they must try to capture the right moments, and then find the right approaches, for bringing together, into a fruitful dialogue, their meanings and interpretations with those of the children.”
Context, in other words, matters more than content. And the physical environment, after adults and peers, is the third teacher.
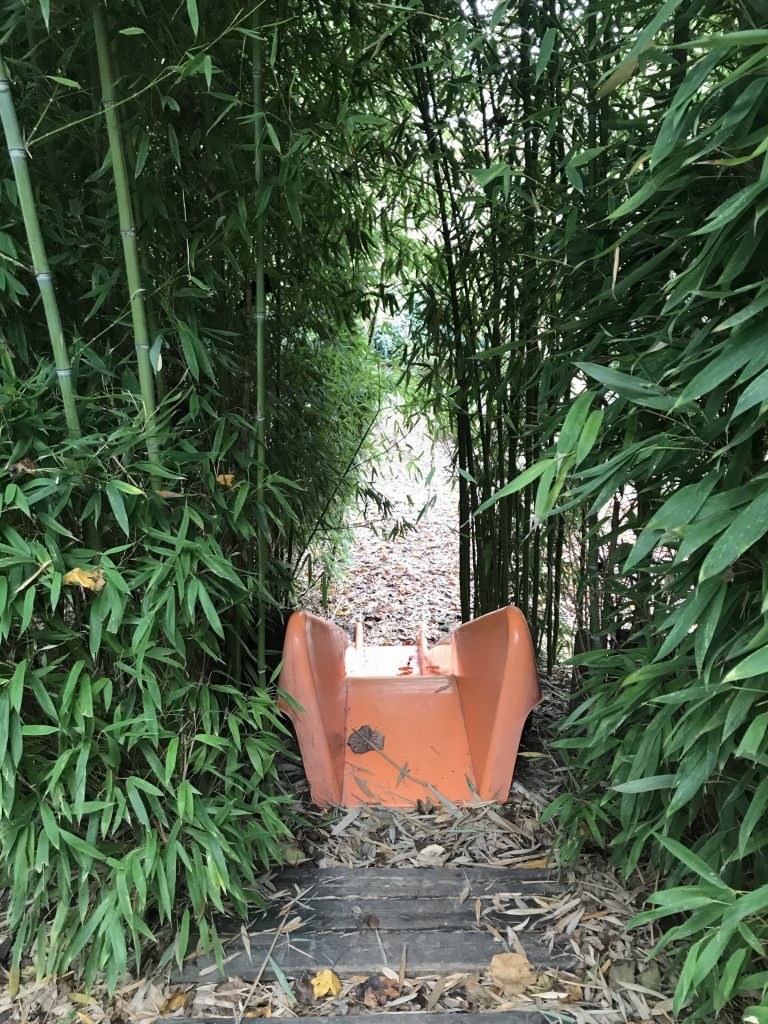
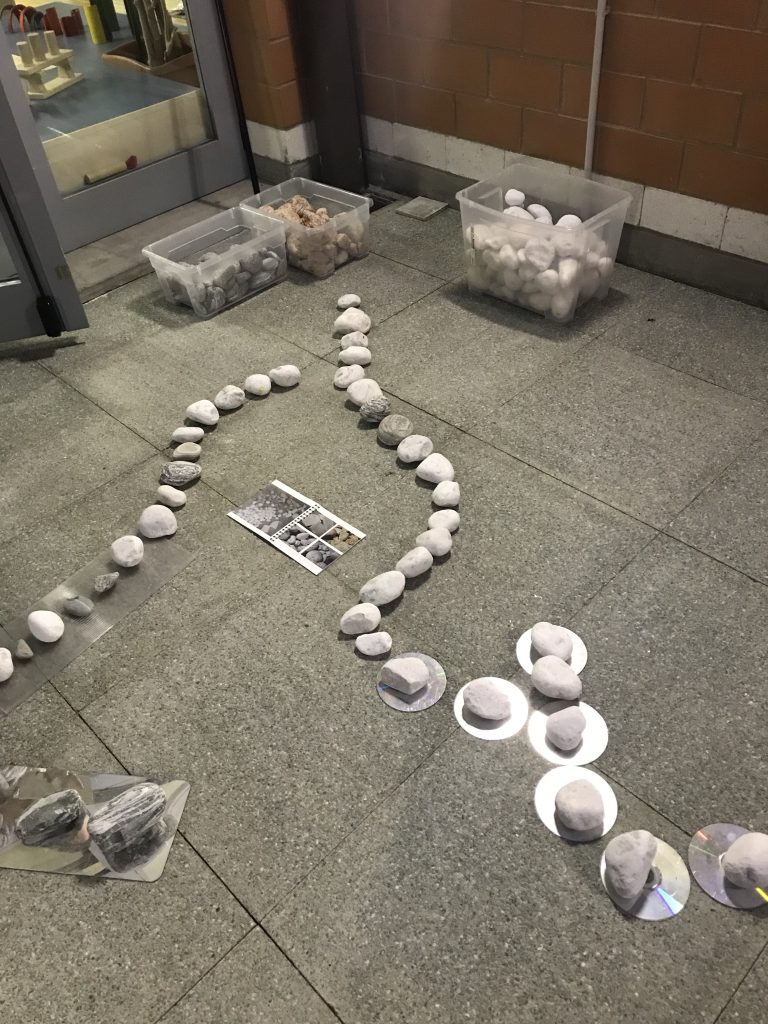
The space is not ancillary; it’s exalted
This is why every Reggio schools feels like a collection of altars. Great care is given to the construction of space, and to the conditions into which children will explore their hundred languages. Intricate patterns of stones snake through an outdoor courtyard, inviting children to continue the pattern, or to begin a new one. A bright orange slide cuts through thick stalks of bamboo, just because. The art materials are ubiquitous, and organized, and easily accessible. And the boundary between inside and outside is always as permeable as possible.
Here, the light is always able to come in.
 It’s why Malaguzzi called the physical environment the Third Teacher. And it’s what led the celebrated psychologist Jerome Bruner to take particular note of a group of four-year-old children who were projecting shadows onto a wall on the day of his visit. “The concentration was absolute, but even more surprising was the freedom of exchange in expressing their imaginative ideas about what was making the shadows so odd, why they got smaller and swelled up or, as one child asked: “How does a shadow get to be upside down?” The teacher behaved as respectfully as if she had been dealing with Nobel Prize winners. Everyone was thinking out loud: “What do you mean by upside down?” asked another child.
It’s why Malaguzzi called the physical environment the Third Teacher. And it’s what led the celebrated psychologist Jerome Bruner to take particular note of a group of four-year-old children who were projecting shadows onto a wall on the day of his visit. “The concentration was absolute, but even more surprising was the freedom of exchange in expressing their imaginative ideas about what was making the shadows so odd, why they got smaller and swelled up or, as one child asked: “How does a shadow get to be upside down?” The teacher behaved as respectfully as if she had been dealing with Nobel Prize winners. Everyone was thinking out loud: “What do you mean by upside down?” asked another child.
“Here we were not dealing with individual imaginations working separately,” Bruner concluded. “We were collectively involved in what is probably the most human thing about human beings, what psychologists and primate experts now like to call ‘intersubjectivity,’ which means arriving at a mutual understanding of what others have in mind. It is probably the extreme flowering of our evolution as humanoids, without which our human culture could not have developed, and without which all our intentional attempts at teaching something would fail.”
The community is not apart; it’s integral
That sense of intersubjectivity is everywhere in Reggio Emilia; it is, in fact, the clearest measure of the school’s longitudinal success. As former mayor Graziano Delrio put it, “We in Reggio Emilia believe that we should manage our cities with the objective of building an equal community, acting for the common good of citizens to guarantee equal dignity and equal rights. We assert the right of children to education from birth. The child is therefore a competent citizen. He or she is competent in assuming responsibility for the city. I often quote this statement by John Adams, the second president of the United States: “Public happiness exists where citizens can take part responsibly for public good and public life. Everywhere, there are men, women, children, whether old or young, rich or poor, tall or short, wise or foolish . . . everyone is highly motivated by a desire of being seen, heard, considered, approved and respected by the people around him and known by him.”


Indeed, the success of Reggio schools would not have been sustained without meaningful partnership and support from its elected leaders. Today, almost 20% of the city’s budget goes towards its early childhood education programs. There is no neighborhood more desirable than another because of the schools; the system has equity throughout. Parents are integral to the success of each school, and play an active role in shared governance. And the spirit of civic participation here, in a city founded by the Romans in the second century B.C., and in a community that can trace its collectivist tendencies back to the craft guilds and communal republics of the medieval 14th century, is what led a mayor of an Industrial city in Northern Italy to proclaim that the infant-toddler centers are “public common spaces where the multitudes aim to become a community of people growing together with a strong sense of the future, a strong idea of participation, of living together, of taking care, one for others. The school expresses the society through which it is generated, but school is also able to generate a new society.”
The bedrock is not love; it’s respect
Finally, this.
It is easy to imagine that all we need to do is love children more, or give them more space, and the rest will take care of itself. But what I witnessed in Reggio was less a case of adults loving children — though surely, they did. Instead, what I witnessed was a level of listening, attention, and care that came from an unwavering belief that all children, even the newest among us, are social beings, predisposed, and possessing from birth a readiness to make significant ties with others, to communicate, and to find one’s place in the world of others.
“We think of school for young children as an integral living organism,” said Malaguzzi, “as a place of shared lives and relationships among many adults and many children. We think of school as a sort of construction in motion, continuously adjusting itself. Either a school is capable of continually transforming itself in response to children, or the school becomes something that goes around and around, remaining in the same spot.”
This is the path. These are the ingredients. But none of it is possible until, as the great theorist David Hawkins once said, we realize that “the more magic gift is not love, but respect for others as ends in themselves, as actual and potential artisans of their own learnings and doings, of their own lives, and thus uniquely contributing, in turn, to their learnings and doings.
“Respect for the young is not a passive, hands-off attitude. It invites our own offering of resources. It moves us toward the furtherance of their lives and thus, even, at times, toward remonstrance or intervention. Respect resembles love in its implicit aim of furtherance, but love without respect can blind and bind. Love is private and unbidden, whereas respect is implicit in all moral relations with others. Adults involved in the world of man and nature must bring that world with them to children, bounded and made safe to be sure, but not thereby losing its richness and promise of novelty.”
Amen.
To learn more about the Reggio Children Foundation, and/or to register for an International Study Group, visit https://www.reggiochildren.it/?lang=en
Recent Comments